Node http request
The http request node is designed to perform HTTP requests to external web services or APIs. It supports multiple HTTP methods, data types, authentication, and flexible management of requests and responses.
Settings for the http request node
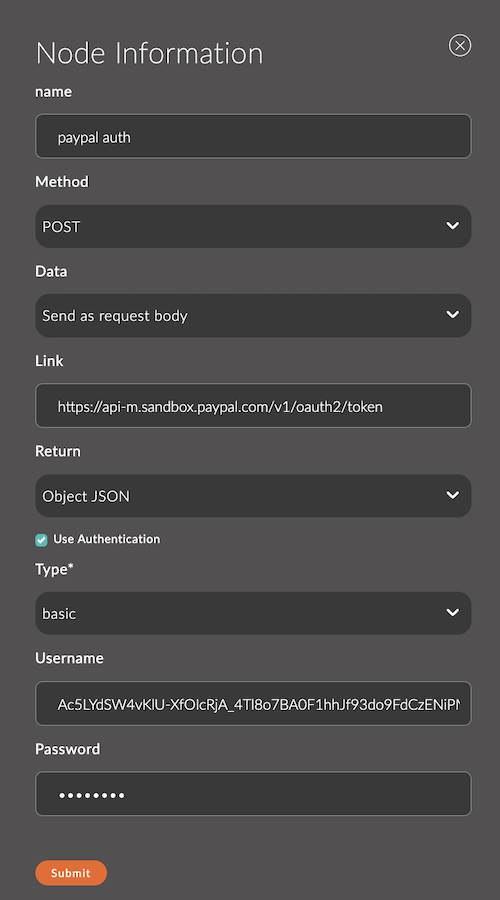
1. Name
A field for specifying the name of the node.
The name is displayed in the workspace and helps to easily identify the node.
If left empty, the node will be called http request.
Example:
- Node name:
Get Weather Data
2. Method
The HTTP method that will be used for the request. The choice of method depends on the type of operation that needs to be performed.
Available methods:
GET: Retrieve data.POST: Send data.PUT: Update data.DELETE: Delete data.PATCH: Partially update data.HEAD: Retrieve response headers.OPTIONS: Get information about the API.
Example:
- Method:
POST
3. Link
A field for specifying a static URL to which the request will be sent.
If the address needs to be set dynamically, it can be passed in msg.url.
Example:
- Link:
https://api.example.com/data
4. Data
Defines how the input data will be added to the HTTP request. The following options are available:
-
Ignore:
The input data will not be used in the request. Themsg.payload, if it exists, will be ignored.Example:
Ifmsg.payloadcontains a JSON object, it will not be included in the request.
-
Add to query parameters:
Data frommsg.payloadwill be converted into query parameters and added to the URL.Example:
Ifmsg.payloadcontains:{
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}If the Link is specified as
http://example.com/api, the final request will be:
GET http://example.com/api?key1=value1&key2=value2.
-
Send as request body:
Data frommsg.payloadwill be sent in the body of the request. This option is suitable for methods such asPOST,PUT, andPATCH, where data is often sent in the body.Example:
Ifmsg.payloadcontains:{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com"
}If the request method is
POST, the data will be sent in the body of the request with the appropriate content.
5. Return
Defines the format in which the node will process the response from the server.
Options:
- UTF-8 string: The response is converted to a string (default).
- Buffer: The response is returned as a
Bufferobject (useful for binary data such as images or files). - JSON: If the server response is in JSON format, it is automatically converted to a JavaScript object.
Example:
- If
JSONis selected, the response:is converted to:{"status": "ok", "value": 42}msg.payload = { status: "ok", value: 42 };
6. Authentication
The node supports built-in authentication mechanisms.
Basic Auth
- Username: Username.
- Password: Password.
Bearer Token
- Token: Access token.
Digest
- Username: Username.
- Password: Password.
Input Data
The http request node accepts a message object msg with the following parameters:
- msg.url: URL for the request (if not specified in the node settings).
- msg.method: HTTP method (if not set in the node settings).
- msg.payload: Body of the request (used for
POST,PUT,PATCHmethods). - msg.headers: HTTP request headers (object).
Output Data
The node returns a msg object with information about the executed request:
- msg.payload: Data response from the server.
- msg.statusCode: HTTP status code of the response (e.g.,
200or404). - msg.headers: Response headers.
- msg.responseUrl: URL to which the request was made.
- msg.error: Description of the error (if the request failed).
Usage Examples
Example 1: Performing a GET request
Node settings:
- Method:
GET - URL:
https://api.weatherapi.com/v1/current.json?key=API_KEY&q=London
Flow:
[inject] ---> [http request] ---> [debug]
Result: The node will return JSON with the current weather.
Example 2: Sending data via POST
Node settings:
- Method:
POST - URL:
https://api.example.com/devices - Data:
JSON
Flow:
[function] ---> [http request] ---> [debug]
Code in the function node:
msg.payload = {
deviceId: "sensor123",
status: "active"
};
msg.headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json" };
return msg;
Result: The data will be sent, and the node will return the server's response.
Example 3: Dynamic URL and authentication
Node settings:
- URL: (leave empty)
Flow:
[function] ---> [http request] ---> [debug]
Code in the function node:
msg.url = "https://api.example.com/user/123";
msg.headers = { Authorization: "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN" };
return msg;
Result: The node will make a request to the specified URL with the authentication token.