Node http response
The http response node is used to send HTTP responses to requests processed by the http in node. It completes the request processing cycle and returns data back to the client.
Settings for the http response node
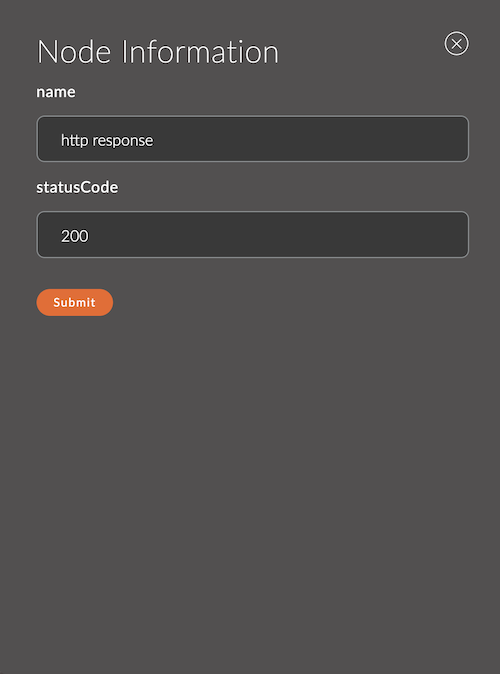
1. Name
A field for specifying the name of the node.
The name is displayed in the workspace and helps to easily identify the node.
If left empty, the node will be called http response.
Example:
- Node name:
Send JSON Response
Fields defined by the incoming message (msg)
The http response node uses the msg object passed to it as input to form the HTTP response. Here are the main parameters:
-
msg.payload
The content of the response. It is sent to the client in the body of the response.Example:
- To send text:
msg.payload = "Hello, World!"; - For a JSON response:
msg.payload = { status: "ok", value: 42 };
- To send text:
-
msg.statusCode
The HTTP status code of the response. If this field is not specified,200 OKis used by default.Examples of status codes:
200— Success.201— Resource created successfully.400— Client error.404— Resource not found.500— Internal server error.
Example:
msg.statusCode = 404; // Resource not found
-
msg.headers
An object defining the headers of the HTTP response. It allows you to specify, for example, the content type, caching, or custom headers.Example:
msg.headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Cache-Control": "no-cache"
};
Usage Examples
Example 1: Sending a successful JSON response
Flow:
[http in] ---> [function] ---> [http response]
Code for the function node:
msg.payload = { success: true, message: "Request processed successfully" };
msg.statusCode = 200;
msg.headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json" };
return msg;
Result:
The client will receive the response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"success": true,
"message": "Request processed successfully"
}
Example 2: Handling an error
Flow:
[http in] ---> [function] ---> [http response]
Code for the function node:
msg.payload = { error: "Invalid request parameters" };
msg.statusCode = 400;
msg.headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json" };
return msg;
Result:
The client will receive the response:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
{
"error": "Invalid request parameters"
}
Example 3: Empty response with a custom status
Flow:
[http in] ---> [http response]
Code in the function node before the http response node:
msg.payload = null; // Empty response body
msg.statusCode = 204; // No content
return msg;
Result:
The client will receive the response:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content