Node http in
The http in node is used to create HTTP endpoints that can handle incoming HTTP requests (GET, POST, PUT, and others). This node serves as the entry point for interacting with external systems via the HTTP protocol.
Important: All specified paths automatically receive the prefix: /api/admin/workflows/endpoints/.
Settings for the http in node
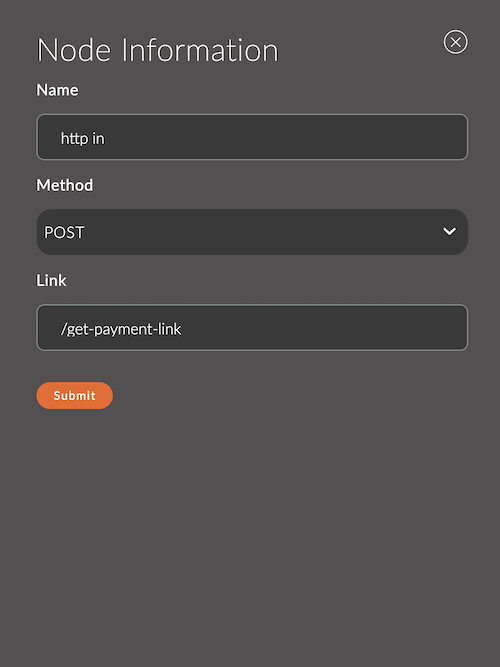
1. Name
A field for specifying the name of the node.
The name is displayed in the workspace and helps easily identify the node.
If left empty, the node will be called http in.
Example:
- Node name:
get payment link
2. Method
The HTTP method that the node will handle. The following options are available:
- GET: Used for retrieving data.
- POST: Used for sending data.
- PUT: Used for updating data.
- DELETE: Used for deleting data.
- PATCH: Used for partially updating data.
- OPTIONS: Used for requests to obtain metadata about the API.
3. Link
Specifies the path (endpoint) for handling requests.
- The path starts with
/. - It can include route parameters, for example:
/data/:id.
Example:
- Link:
/get-payment-link - Link with parameter:
/get-payment-link/:orderId
Format of the incoming message
When a request is received at the specified path with the selected method, the http in node creates a message msg with the following properties:
-
msg.req: Contains the HTTP request object, including headers, parameters, body, and other data.msg.req.params: Route parameters (e.g.,:idin/api/data/:id).msg.req.query: GET request parameters.msg.req.body: The body of the request (for POST, PUT, and PATCH methods).
-
msg.res: An object for managing the HTTP response. It is usually passed to thehttp responsenode to send a response back to the client.
Example usage
Example 1: Handling a GET request
Scenario: Returning temperature data.
Node settings:
- Method:
GET - Link:
/temperature
Flow:
[http in] ---> [function] ---> [http response]
Code for the function node:
msg.payload = { temperature: 22.5, unit: "Celsius" };
return msg;
Result: The client that sends a GET request to /api/admin/workflows/endpoints/temperature will receive a JSON response:
{
"temperature": 22.5,
"unit": "Celsius"
}
Example 2: Handling a POST request
Scenario: Receiving and saving data from a device.
Node settings:
- Method:
POST - Link:
/data
Flow:
[http in] ---> [function] ---> [http response]
Code for the function node:
// Reading data from the request body
const data = msg.req.body;
msg.payload = { status: "success", receivedData: data };
return msg;
Result: The node will accept data from the body of the POST request and return a confirmation response.
Example 3: Using route parameters
Scenario: Retrieving data by device ID.
Node settings:
- Method:
GET - Link:
/device/:id
Flow:
[http in] ---> [function] ---> [http response]
Code for the function node:
const deviceId = msg.req.params.id;
msg.payload = { deviceId: deviceId, status: "active" };
return msg;
Result:
{
"deviceId": "123",
"status": "active"
}